Are you curious about the impact of public and private charging infrastructure on electric vehicles? Look no further than Currentcarreport.com, your ultimate online destination for all things related to EVs. Our comprehensive guide offers insights into the latest models, battery technology breakthroughs, and global market trends. Additionally, we provide an exhaustive directory of charging stations, reviews on the best home chargers, and updates on fast-charging infrastructure advancements. Whether you’re an EV enthusiast, potential buyer, or simply interested in the electric shift in transportation, EV Nexus is here to be your guiding light in navigating the future of mobility. In this article, we will explore the differences between public and private charging infrastructure, shedding light on their respective impacts on electric vehicles.
The Impact of Public and Private Charging Infrastructure on Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years as a more sustainable and environmentally friendly mode of transportation. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, the development of charging infrastructure plays a crucial role in the widespread adoption and success of these vehicles. In this article, we will explore the impact of both public and private charging infrastructure on EVs, discussing their benefits, challenges, and the role of government and policy in their development.
Introduction to Public and Private Charging Infrastructure
1.1 Definition and Overview of Public Charging Infrastructure
Public charging infrastructure refers to the network of charging stations available to the general public. These charging stations are typically located in public areas such as parking lots, shopping centers, and along highways, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles while on the go. Public charging infrastructure includes both slow and fast chargers, with fast chargers being capable of charging an EV to 80% capacity within 30 minutes.
1.2 Definition and Overview of Private Charging Infrastructure
In contrast, private charging infrastructure pertains to charging stations installed at private residences or workplaces. These charging stations provide EV owners with the convenience of charging their vehicles overnight or during working hours, eliminating the need to rely solely on public charging infrastructure. Private charging infrastructure is typically slower than fast public chargers but can still fully charge an EV overnight.
1.3 Importance of Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles
The availability and accessibility of charging infrastructure are crucial factors influencing the adoption and usage of EVs. Without a well-developed charging infrastructure, EV owners may face challenges in finding charging stations, resulting in range anxiety and limited usage. The development of both public and private charging infrastructure is vital in addressing these concerns and promoting the widespread adoption of EVs.
This image is property of cdn.gminsights.com.
Benefits of Public Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles
2.1 Extended Driving Range for EV Owners
One of the primary benefits of public charging infrastructure is the extension of the driving range for EV owners. Public charging stations allow EV drivers to charge their vehicles while on long trips or in areas where private charging is not feasible. By providing charging stations along highways and in public areas, EV drivers can confidently embark on longer journeys, knowing that they have access to charging infrastructure when needed.
2.2 Convenience and Accessibility for EV Users
Public charging infrastructure offers convenience and accessibility to all EV users. With an increasing number of charging stations available, EV owners can easily locate and utilize these charging stations, making it more convenient to charge their vehicles. The widespread availability of public charging infrastructure also eliminates the need for EV drivers to rely solely on home or workplace charging, providing them with more flexibility and freedom in their driving habits.
2.3 Addressing Range Anxiety and Boosting Confidence in EVs
Range anxiety, the fear of running out of charge before reaching a destination, is a significant concern for many potential EV owners. Public charging infrastructure plays a crucial role in addressing this anxiety by providing EV drivers with the peace of mind that they can charge their vehicles whenever needed. The presence of charging stations in various locations alleviates concerns about running out of charge, thereby boosting confidence in EV ownership and encouraging more individuals to switch to electric vehicles.
2.4 Increasing the Appeal and Market Demand for Electric Vehicles
The availability of public charging infrastructure also helps to increase the appeal and market demand for EVs. As more charging stations become accessible, the perceived inconvenience and limitations of EV ownership are diminished. This, in turn, attracts more potential buyers, as the concern about charging infrastructure becomes less daunting. The growth of public charging infrastructure contributes to the overall growth and adoption of EVs, creating a positive impact on the environment and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Challenges and Limitations of Public Charging Infrastructure
3.1 Insufficient Number of Charging Stations
One of the significant challenges of public charging infrastructure is the insufficient number of charging stations. In some areas, the demand for charging stations may exceed the available supply, resulting in long wait times or the unavailability of charging stations during peak hours. This can frustrate EV owners and deter potential buyers, as the inconvenience of waiting or the uncertainty of finding an available charging station may outweigh the benefits of owning an EV.
3.2 Inconsistent Charging Speeds and Compatibility
Public charging infrastructure also faces challenges regarding inconsistent charging speeds and compatibility. Different charging stations may have varying charging speeds, making it difficult for EV owners to plan their charging sessions optimally. Additionally, compatibility issues between charging station connectors and EV models can create a barrier for EV owners, especially when traveling to areas with different charging standards. The standardization of charging speeds and connectors is essential to ensure a seamless charging experience for all EV owners.
3.3 Cost and Pricing Models for Public Charging
The cost and pricing models for public charging can pose challenges for EV owners. Some charging stations may have high charging fees, making it more expensive for EV owners to charge their vehicles in public compared to charging at home. The lack of uniform pricing across charging stations and transparency regarding charging costs can create confusion and uncertainty for EV owners. Establishing fair and transparent pricing models is crucial to promote the usage of public charging infrastructure.
3.4 Reliability and Downtime of Public Charging Stations
The reliability and downtime of public charging stations are significant concerns for EV owners. Breakdowns, maintenance, or other technical issues can render charging stations temporarily unavailable, causing inconvenience and frustration for EV owners who rely on these stations for charging. Ensuring regular maintenance and prompt repairs are necessary to minimize downtime and ensure the reliability of public charging infrastructure.

This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.
Advantages of Private Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles
4.1 Convenience and Accessibility of Charging at Home or Work
Private charging infrastructure offers convenience and accessibility for EV owners. With a charging station installed at home or work, EV owners can conveniently charge their vehicles overnight or during working hours. This eliminates the need to rely solely on public charging infrastructure, allowing EV owners to have greater control and flexibility over their charging habits.
4.2 Lower Cost of Charging compared to Public Infrastructure
Charging an EV using private infrastructure is often more cost-effective compared to utilizing public charging stations. The cost of electricity for home or workplace charging is typically lower than the charging fees of public stations, enabling EV owners to save money in the long run. The lower cost of charging makes EV ownership more financially appealing, especially for individuals who can charge their vehicles predominantly at home or work.
4.3 Control and Reliability of Charging Station Ownership
Owning a private charging station provides EV owners with control and reliability. Unlike public charging infrastructure, EV owners do not have to worry about the availability or functionality of charging stations. With a private charging station, EV owners have the reassurance that their vehicles can be charged reliably and consistently, without the inconvenience of potential downtime or technical issues.
Drawbacks and Challenges of Private Charging Infrastructure
5.1 Limited Availability for EV Owners without Private Spaces
One of the significant drawbacks of private charging infrastructure is the limited availability for EV owners who do not have access to private spaces. Individuals living in apartments, condominiums, or urban areas without dedicated parking spaces may face difficulties in installing private charging stations. This limitation can discourage some potential EV buyers, as the lack of private charging infrastructure may significantly impact their ability to own and use an EV.
5.2 Upfront Costs and Installation Challenges for Home Charging
The upfront costs and installation challenges associated with home charging can pose obstacles for some EV owners. Installing a private charging station requires appropriate wiring and electrical infrastructure, which may necessitate upgrades to existing electrical systems. The expenses involved in acquiring and installing the charging equipment can be substantial, especially for individuals who do not have existing electrical infrastructure suitable for EV charging.
5.3 Dependency on Residential Infrastructure Capacity and Upgrades
Private charging infrastructure heavily relies on the capacity of residential electrical infrastructure. If the existing infrastructure is not equipped to handle the additional load from EV charging, it may require upgrades to accommodate the increased demand. Upgrading residential infrastructure can be a costly and time-consuming process, potentially deterring some EV owners from installing private charging stations.
5.4 Lack of Standardization in Private Charging Equipment
Another challenge of private charging infrastructure is the lack of standardization in charging equipment. Unlike public charging stations that adhere to specific industry standards, private charging equipment varies in terms of charging speeds, connectors, and compatibility. This lack of standardization can cause confusion and inconvenience for EV owners when accessing private charging stations that may not be compatible with their vehicles. Promoting standardization in private charging equipment is critical to ensure a streamlined and user-friendly charging experience.
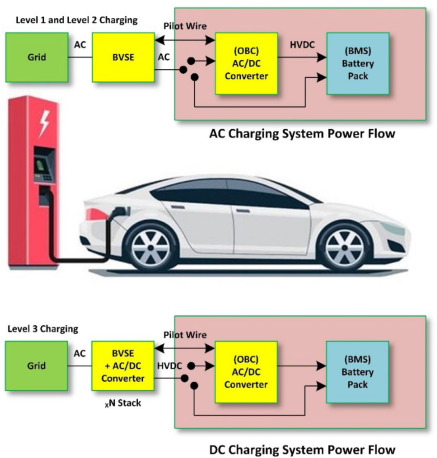
This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.
The Role of Government and Policy in Public Charging Infrastructure
6.1 Government Incentives and Support for Charging Infrastructure
Government incentives and support play a crucial role in the development of public charging infrastructure. Governments around the world are implementing various incentives, such as grants, tax credits, and subsidies, to encourage the installation and expansion of public charging stations. These incentives help offset the costs associated with charging infrastructure development and promote private investments in expanding the charging network.
6.2 Regulation and Standardization for Public Charging Stations
Regulation and standardization are essential in ensuring the quality and reliability of public charging stations. Governments and regulatory bodies establish regulations and standards for public charging infrastructure, covering aspects such as safety protocols, charging speeds, and compatibility. Standardization promotes interoperability and a consistent charging experience for EV owners, regardless of the charging station they utilize.
6.3 Licensing and Permitting Processes for Charging Infrastructure
Governments often implement licensing and permitting processes to regulate the installation and operation of public charging infrastructure. These processes ensure that only authorized entities or individuals can set up and maintain charging stations, minimizing the risk of improper installations or unsafe charging practices. Licensing and permitting help maintain the quality and reliability of public charging infrastructure while also ensuring compliance with local regulations and standards.
6.4 Collaboration with Stakeholders and Industry Players
Government involvement in public charging infrastructure development often involves collaboration with stakeholders and industry players. Governments work closely with electric utilities, charging station operators, automakers, and technology providers to establish partnerships and facilitate the expansion of the charging network. Such collaborations help leverage the expertise and resources of various stakeholders, accelerating the development and deployment of public charging infrastructure.
Public-Private Partnership in Charging Infrastructure Development
7.1 Collaborative Funding and Investment Opportunities
Public-private partnerships are instrumental in allocating financial resources for charging infrastructure development. By combining public funding and private investments, governments and private entities can pool resources to fund the installation and expansion of charging stations. Collaborative funding models create sustainable financing mechanisms, ensuring the continued growth and maintenance of public charging infrastructure.
7.2 Joint Planning and Strategic Deployment of Charging Infrastructure
Public-private partnerships involve joint planning and strategic deployment of charging infrastructure. Governments and private entities collaborate to identify areas with high demand for charging stations and strategically deploy them to cater to the needs of EV owners. This collaborative approach ensures that charging infrastructure is efficiently distributed, maximizing the benefits for EV users and optimizing the utilization of resources.
7.3 Sharing of Data and Information for Infrastructure Improvement
Public-private partnerships facilitate the sharing of data and information for infrastructure improvement. By exchanging data on charging patterns, utilization rates, and user preferences, governments and private entities can identify areas of improvement and optimize charging infrastructure accordingly. This data-driven approach leads to more efficient and effective charging infrastructure, further enhancing the user experience for EV owners.
7.4 Case Studies and Successful Examples of Public-Private Partnerships
Several successful examples of public-private partnerships in charging infrastructure development exist worldwide. For instance, the collaboration between the City of Los Angeles and private charging companies has led to the installation of a comprehensive network of public charging stations throughout the city. This partnership has significantly increased the accessibility and usability of EV charging in Los Angeles, encouraging more individuals to adopt electric vehicles.

This image is property of afdc.energy.gov.
The Impact of Public Charging Infrastructure on EV Adoption
8.1 Increased Confidence in EV Ownership and Usage
Public charging infrastructure plays a vital role in increasing confidence in EV ownership and usage. With a well-developed network of charging stations, EV owners can feel confident that they have access to charging infrastructure wherever they go. This confidence eliminates range anxiety and reduces the perceived limitations of EV ownership, leading to increased adoption and usage of electric vehicles.
8.2 Addressing Range Anxiety and Expanding Adoption beyond Urban Areas
Range anxiety is a significant barrier to EV adoption, particularly for individuals living in rural or remote areas. Public charging infrastructure helps address this anxiety by providing charging stations in areas where private charging may not be feasible. The availability of charging stations along highways and in non-urban areas allows EV owners to travel with peace of mind, knowing that they can charge their vehicles whenever necessary. This expansion of charging infrastructure promotes the adoption of EVs in areas that were previously not conducive to electric mobility.
8.3 Promoting Electric Mobility for All Socioeconomic Strata
The development of public charging infrastructure also promotes electric mobility for individuals across different socioeconomic strata. By making charging stations accessible in public areas, EV ownership becomes more inclusive, benefiting individuals who may not have access to private charging infrastructure. Public charging stations provide an equal opportunity for all individuals to adopt and utilize electric vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future of transportation.
The Impact of Private Charging Infrastructure on EV Adoption
9.1 Enhancing Convenience and Accessibility for EV Owners
Private charging infrastructure enhances convenience and accessibility for EV owners. By having a charging station at home or work, EV owners can charge their vehicles at their convenience, without the need to rely on public charging infrastructure. The ease of access to charging facilities encourages individuals to switch to electric vehicles, as they can seamlessly incorporate charging into their daily routines.
9.2 Addressing the Needs of Urban Dwellers and Commuters
Private charging infrastructure specifically caters to the needs of urban dwellers and commuters. In urban areas, public charging infrastructure may not be as readily available or convenient due to limited parking spaces or high demand. Private charging stations installed at residences and workplaces overcome these challenges, providing EV owners with a reliable and accessible charging option. These charging options are particularly advantageous for individuals who rely on their vehicles for daily commuting.
9.3 Promoting Sustainable Lifestyles with Green Energy Integration
Private charging infrastructure supports the integration of green energy sources, promoting sustainable lifestyles. By utilizing solar panels or other renewable energy sources to power private charging stations, EV owners can further reduce their carbon footprint. The combination of electric vehicles and renewable energy generation contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system, showcasing the potential for a greener future.
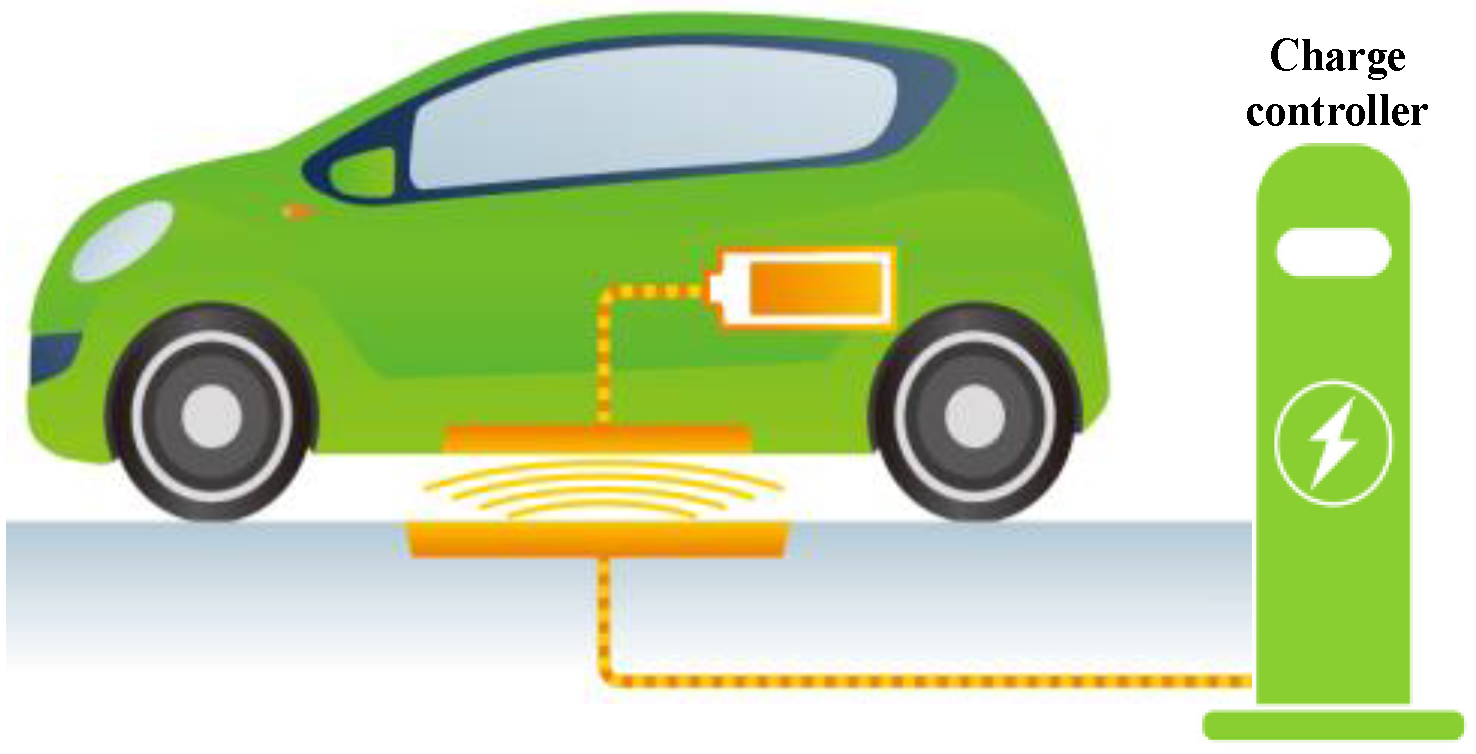
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Comparison of Public and Private Charging Infrastructure
10.1 Availability and Accessibility
Public charging infrastructure offers widespread availability, ensuring that EV owners have access to charging stations in various locations. Private charging infrastructure, on the other hand, is limited to EV owners with private spaces or access to workplace charging. While public charging is more accessible to a larger population, private charging provides greater convenience for EV owners with dedicated charging stations at home or work.
10.2 Charging Speed and Reliability
Public charging infrastructure typically offers faster charging speeds compared to most private charging stations. Fast charging stations along highways and in public areas enable EV owners to quickly charge their vehicles, making long-distance travel more feasible. Private chargers, although slower, provide reliability and consistency in charging, as EV owners have control over their charging equipment and can rely on it for daily usage.
10.3 Cost and Pricing
In terms of cost, private charging infrastructure is generally more affordable than public charging, mainly due to lower electricity rates at residential or workplace settings. Public charging stations often charge higher fees, which can add up over time for frequent EV users. However, it is essential to consider the upfront costs of installing private charging infrastructure, which can be substantial compared to utilizing public charging stations.
10.4 Coverage and Distribution
Public charging infrastructure has a wider coverage and distribution compared to private charging stations. Public charging stations are strategically placed along highways, in parking lots, and commercial areas, ensuring that EV owners can access them while on the go. Private charging infrastructure, although convenient for individual EV owners, may not be as extensive in terms of coverage and distribution.
Future Trends and Innovations in Charging Infrastructure
11.1 Advanced Charging Technologies
The future of charging infrastructure holds promising advancements in charging technologies. Fast-charging stations capable of delivering even higher power levels will become more prevalent, reducing charging times significantly. Wireless charging technology is also being developed, eliminating the need for physical connectors and simplifying the charging process. These advanced charging technologies will shape the future of EV charging infrastructure, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
11.2 Integration with Smart Grids and Renewable Energy
The integration of charging infrastructure with smart grids and renewable energy sources is another emerging trend. By connecting charging stations to the grid, EV charging can be optimized based on electricity demand, availability, and cost. Additionally, incorporating renewable energy sources into charging infrastructure further promotes sustainability and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
11.3 Expansion of High-Power Charging Networks
As EV adoption continues to grow, the expansion of high-power charging networks will become increasingly important. High-power charging networks, capable of delivering ultra-fast charging speeds, allow for shorter charging times and enhanced convenience for EV owners. The development of these networks, combined with advancements in battery technology, will further accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
11.4 Integration into Smart City Infrastructure
Charging infrastructure is expected to be integrated into broader smart city initiatives. Smart city infrastructure aims to use technology and data to enhance urban living, and EV charging will play a significant role in this transformation. Charging stations can be integrated with city infrastructure, such as parking management systems and traffic control, to optimize operations and promote seamless electric mobility within smart cities.
Conclusion
The impact of public and private charging infrastructure on electric vehicles is undeniable. The development of a well-planned and comprehensive charging network is crucial in promoting EV adoption and addressing the challenges associated with electric mobility. Public charging infrastructure extends the driving range of EV owners, boosts confidence in EV ownership, and expands the appeal and market demand for electric vehicles. Private charging infrastructure enhances convenience and accessibility for EV owners, particularly in urban areas and for daily commuting. Collaborative efforts between governments, stakeholders, and industry players, along with future trends and innovations, will further enhance the charging experience for EV owners and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.

